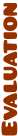
Bottom
Additionally, whenever a set of answers is returned, it is important to be able to rank them. This component applies a range of ranking measures which take into account:
a) criteria referring to the Semantic Similarity (are the answers from different OTs similar interpretations?),
b) criteria referring to the PowerAqua confidence of the mapping between QTs and their OTs (how good translations are the OTs used to derive the answer?), and
c) criteria referring to the popularity (frequency), of the answer (which answer is returned by the most ontologies?).
This initial evaluation is conducted using our own benchmark (The construction of this benchmark was needed due to the lack of SW standard evaluation benchmarks comprising all the required information to judge the quality of the current semantic search methods) which comprises:
- Ontologies and Knowledge Bases: We collected around 4GBs of data stored in 130 Sesame repositories. Each repository contains one or more semantic sources. We have collected in total more than 700 documents. The dataset includes high-level ontologies, e.g., ATO, TAP, SUMO, DOLCE and very large ontologies, e.g., SWETO (around 800,000 entities and 1,600,000 relations) or the DBPedia Infoboxes (around 1GB of metadata). This set of ontologies is stored in several online Sesame repositories. Even though PowerAqua can access larger amounts of SW data through Watson, in this experiment we decided to use a substantial static dataset in order to make these experiments reproducible. All the repositories used in this evaluation are online at Sesame repositories (no longer available).
- Queries: We collected a total of 40 questions selected from the PowerAqua website and from previous PowerAqua evaluations that focused on its mapping capabilities [10]. These are factual questions that PowerAqua maps into several OTs, each of them producing partial answers. Merging and ranking is needed for these queries to generate a complete answer, or to rank between the different interpretations.
- Jugements : In order to evaluate the merging and ranking algorithms a set of jugements over the retrieved answers is needed. To perform this evaluation two ontology engineers provided a True/False manual evaluation of answers for each query.
The aim of the ranking measures presented here is to: a) assign a score to each individual answer and b) cluster the set of answers according to their score. The cluster ranked at position one (C@1) represents the best subset of results according to the chosen ranking method. In here we list the questions used for this evaluation. The tables at the end show (1) the level of filtering performed by the merging algorithm over the initial set of answers retrieved by PowerAqua and (2) Precision and Recall at C@1 (with respect to the baseline) for the three proposed ranking algorithms and their combination applied to the final set of answers obtained after the merging process
The merging algorithm is able to filter out up to 91% (32% on average) for union-based queries, and up to 99% (93% on average) for intersection based queries (with a 94% precision and 93% recall in the fusion algorithm) The best ranking algorithm (ranking by confidence) is able to obtain an average of 96% precision for union queries and 99% for intersection queries.
Questions
Q1. What are the main rivers in Russia
Q2. Show me the films of Jenifer Aniston
Q3. Which Russian rivers flow into the Black Sea?
Q4. Which Russian rivers flow into the Azov Sea?
Q5. Give me the paper(s) written by Enrico Motta
Q6. Who play in Nirvana?
Q7. Give me all cities of Spain.
Q8. Which countries speak arabic and english language?
Q9. Which languages are spoken in Islamic countries
Q10. Which languages are spoken in countries in Eastern Europe
Q11. which rivers flow in european countries.
Q12. Give me mountains in countries near the black sea
Q13. Show me the publications of Enrico Motta.
Q14. Find me university cities in Japan
Q15. Which countries are members of the EU?
Q16. Give me the cities which are in texas.
Q17. How many cities does rhode island have?
Q18. List me all rivers crossing USA.
Q19. Give me cities in virginia.
Q20. Find all the lakes in California.
Q21. What states are next to arizona?
Q22. What is the capital of maryland?
Q23. Which state is kalamazoo in?
Q24. Where is san diego?
Q25. How many states are there in USA?
Q26. tell me all the projects related to academics in akt.
Q27. how many cities in the usa are located in Georgia?
Q28. Give me a French restaurant in alameda?
Q29. Where is houston?
Q30. What mountains are in alaska?
Q31. Which organizations participates in humanitarian aid?
Q32. List me all films with Tim Robbins and Morgan Freeman
Q33. Which RBA banks are situated in Switzerland
Q34. Who starts in Bruce Almighty
Q35. what are the publications of Marta Sabou or/and Frank Van Harmelen?
Q36. who belongs to the open university
Q37. In what state is salem?
Q38. San antonio is in what state?
Q139. Name the president of Russia
Q40. which countries are traversed by the rivers that flow into the caspian sea?
Top Results for UNION queries:
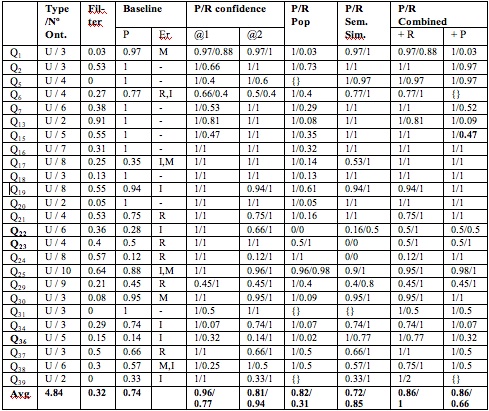
Results for INTERSECTION queries:
The causes of the merging algorithm leading to irrelevant results in the final answers are:
(1) Incorrect modeling of the ontological elements in the OTs that lead to the answer (M). For instance in Q30: what mountains are in Alaska?, the instance Germany is given as an answer because it is defined as rdf:type {country, mountain} in one of the ontologies.
(2) An inaccurate semantic interpretation given by PowerAqua (I). For instance Q36: who belongs to the Open University?. Among OTs representing people that work for the Open University, there is an OT : (organization, type, open universities).
(3) Retrieval of irrelevant answers (R). E.g., the answer Houston to Q29: Where is Houston?
